The Ultimate Guide to Building Strong Foundations for Your Bamboo Structure
By Sai Goutham | September 13, 2021 | Construction -

Foundations are one of the most important structural elements in the bamboo building process. Foundations keep the building protected against natural forces and calamities such as earthquakes, floods and strong winds. The strength and stability of the building relies upon how well the foundations of the building are designed and built.
In bamboo buildings, foundations not only stabilize the building but they also protect the bamboo from moisture in the soil as well as to avoid insects like termites from eating away at the bamboo.
There are two stages of building strong foundations for bamboo buildings. First, is the design: a consultation with a structural engineer is recommended to determine the exact dimensions and the right grade of concrete that needs to be used based on the building, the soil present on site, and other load factors. The second stage is building the foundations on-site.
In this article, we will share the process of building foundations for bamboo structures on-site:
- Mark the foundation points
- Cast the foundations
- Add a moisture barrier
- Fasten the bamboo poles to the foundations
1. Mark the foundation points
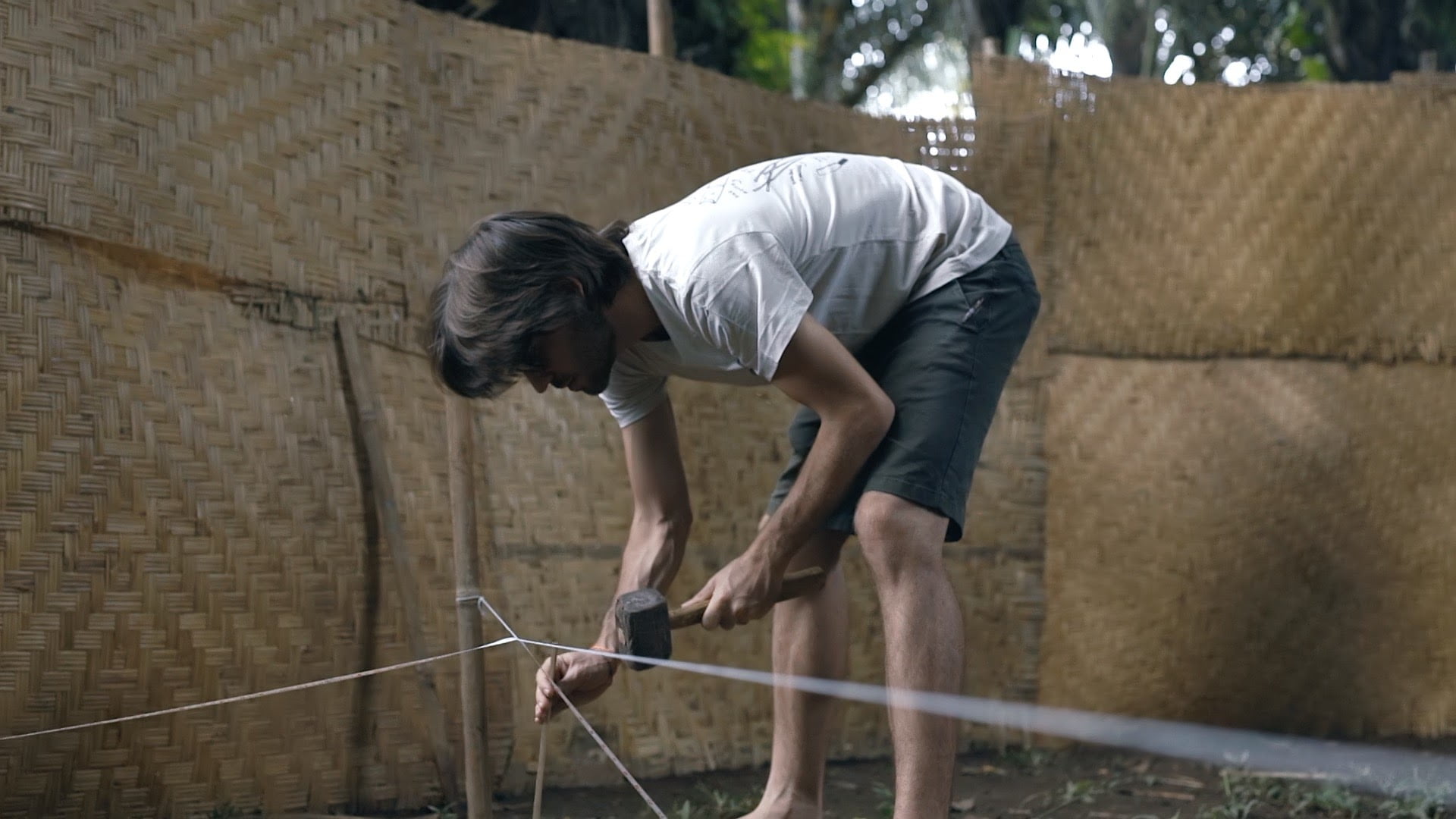
Begin by cleaning your site before starting the construction of your foundations. Once the site is cleaned, mark the foundation points by first producing a foundation layout and detailed construction drawings with all the measurements.
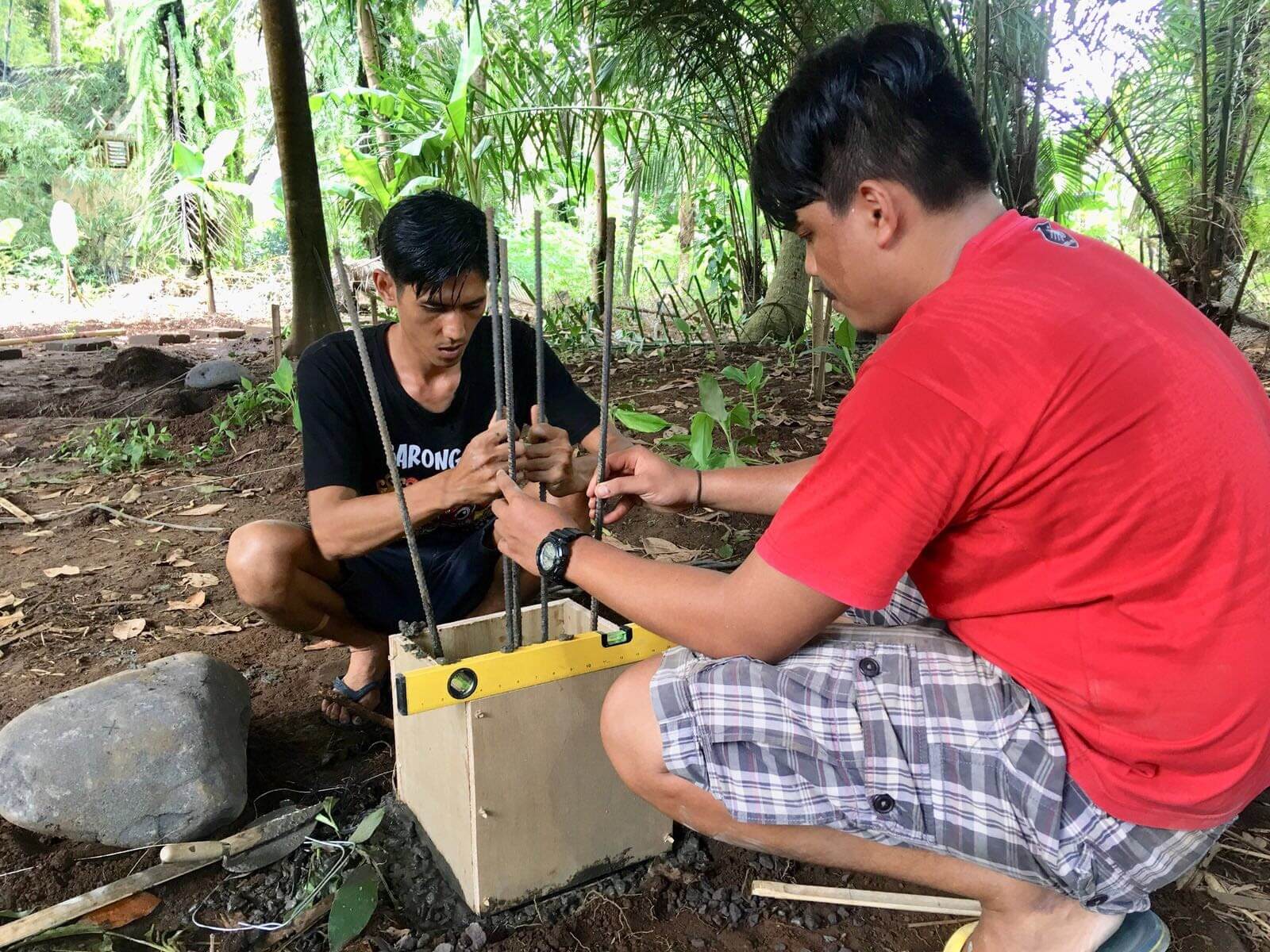
Use bamboo pegs, steel rods, and white strings to mark the foundation points based on your drawings. Keep in mind that marking on contoured sites is a bit difficult and has to be done more carefully compared to flat sites. Once all the markings are done, it is time to break ground according to the dimensions of the foundations to pour concrete.

2. Cast the foundations
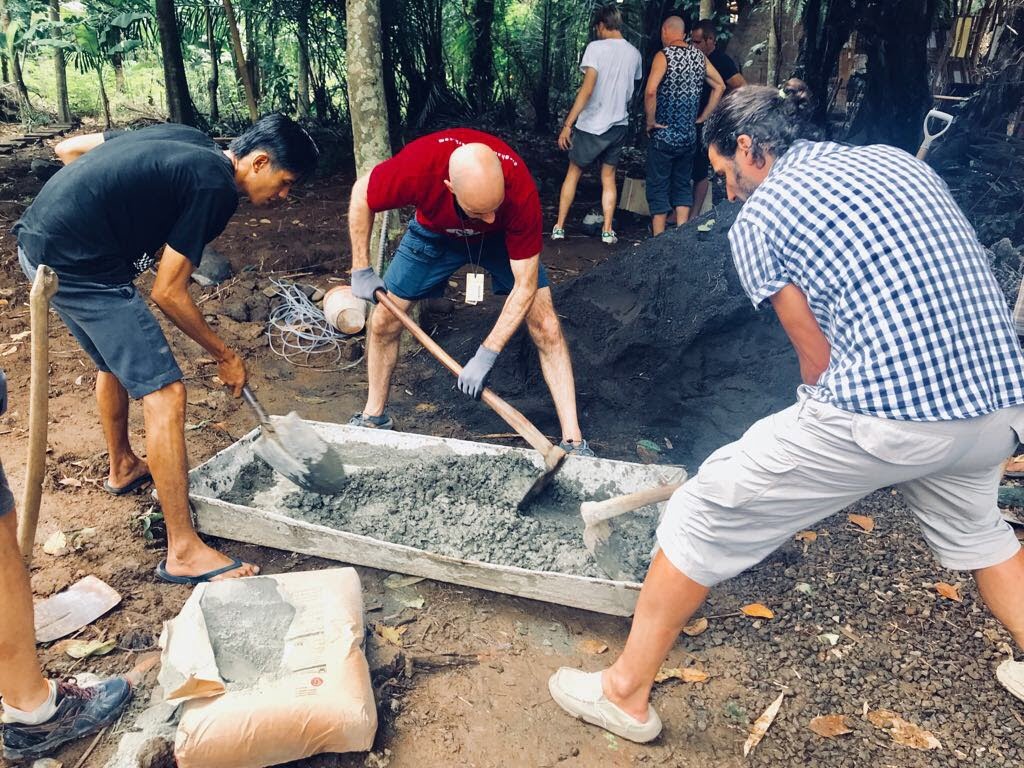
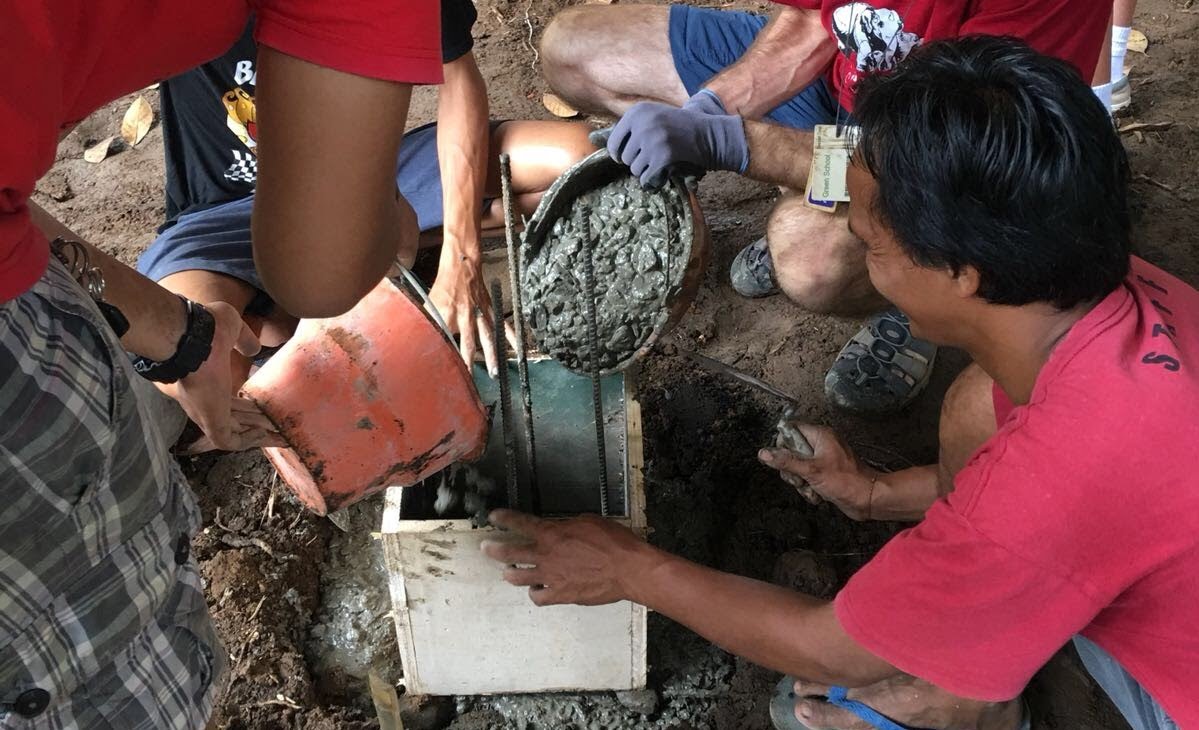
We commonly use reinforced cement concrete(R.C.C) pile foundations for our bamboo buildings. To pour the concrete you need the construction tools to prepare the mix. Cement, sand and gravel are mixed in the ratio according to the engineer’s suggested concrete grade (M15, M20, etc.).
First thing is to add the rebar (steel reinforcement rods) in the dug foundation points and place them steadily in the center of the foundation holes. Then pour the concrete mixture over the rebars, into the foundation points. For the footings that help to raise the height of the building from the ground level, use shuttering like wooden, steel, or PVC pipes over the foundation points to cast the footings along with the foundations. After casting the foundations, they will need to be left to cure and watered everyday for 14-28 days in order to properly set.



3. Add a moisture barrier
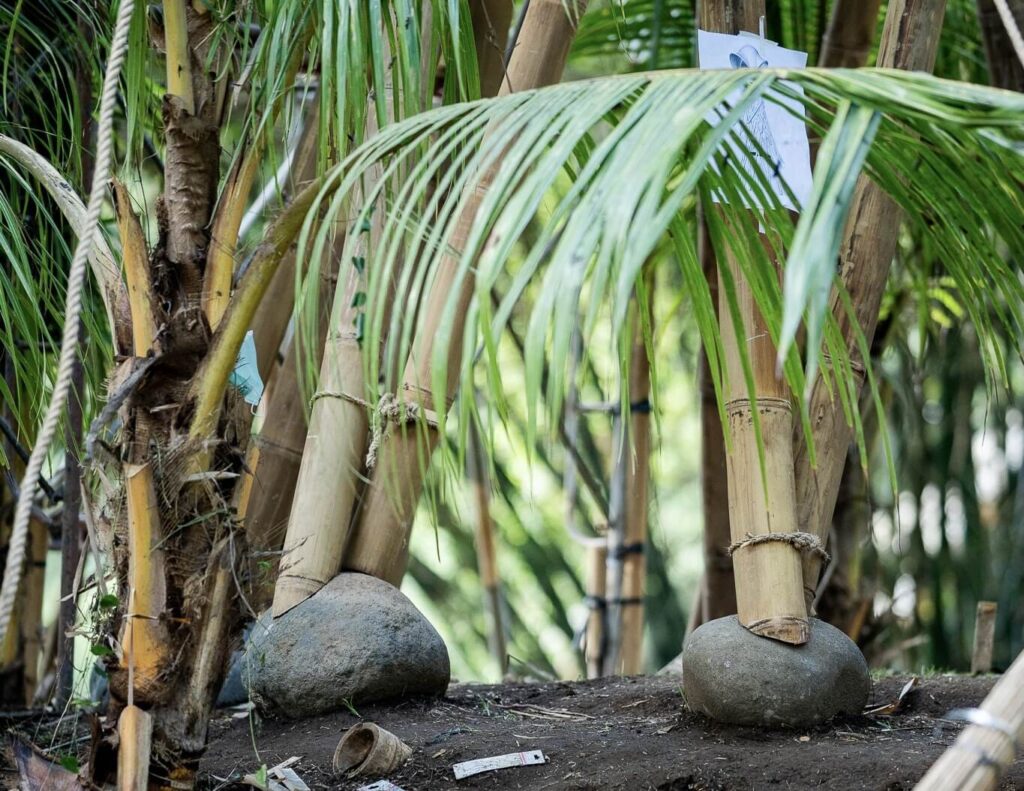
Once the foundations have been cured and are dry, we recommend adding a moisture barrier over the foundations because concrete bases absorb moisture and are friendly to mold growth.
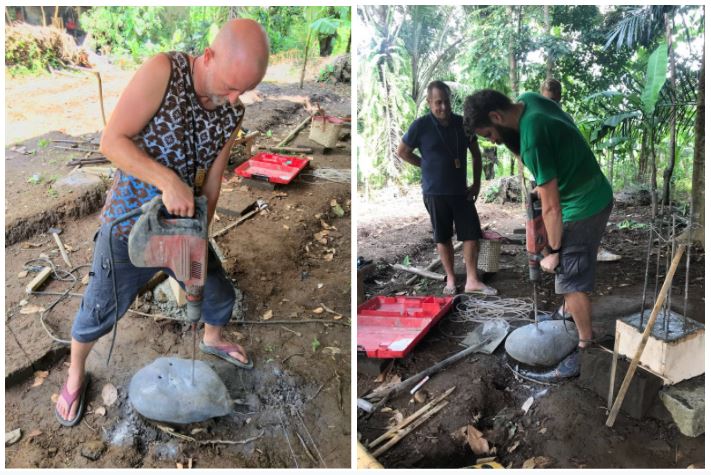
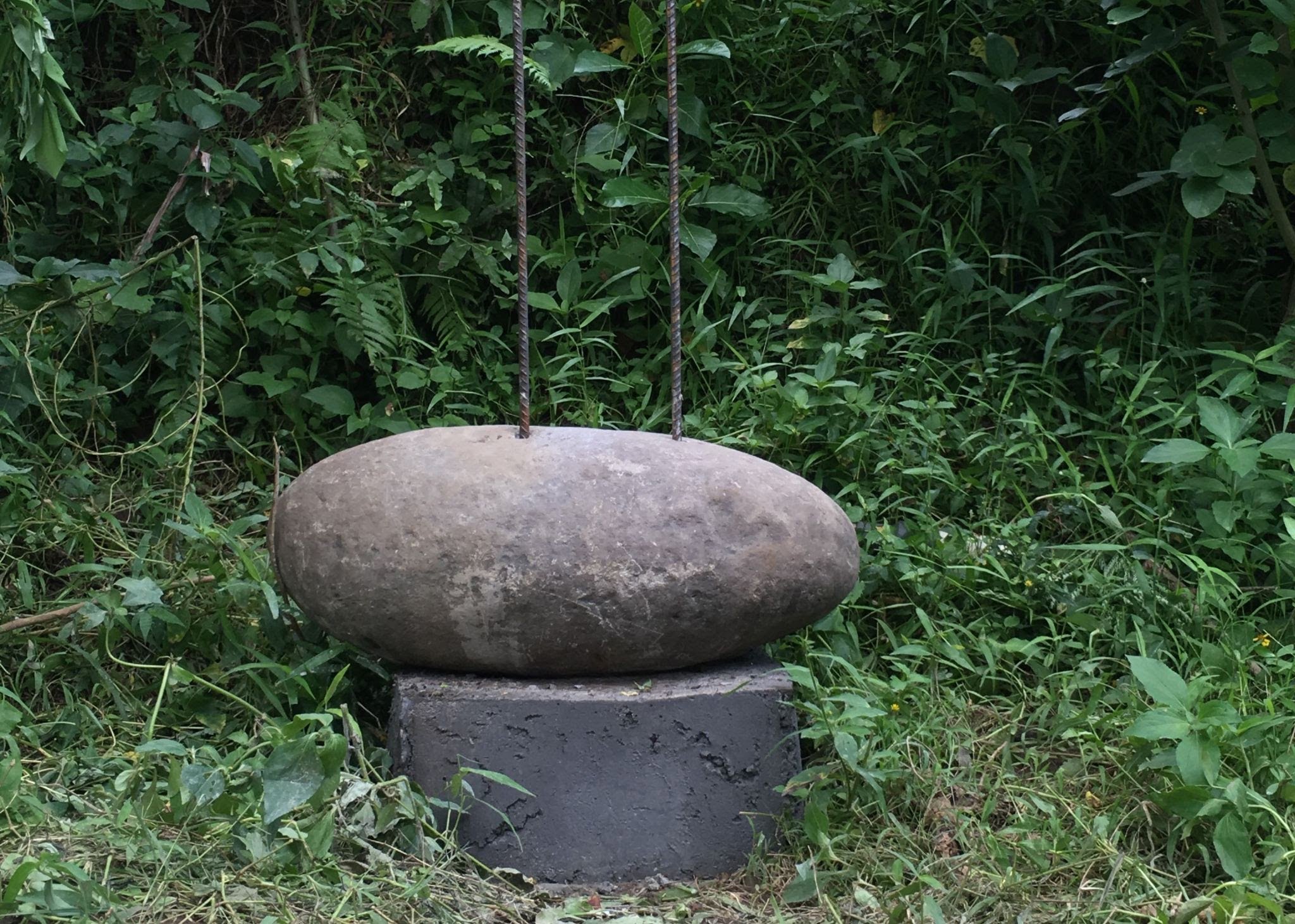
We normally use natural stones; they act both as a moisture barrier and as an aesthetic element. If you are using a natural stone as a moisture barrier you will need a heavy stone hammer drill to puncture the stones, so that they can be threaded easily onto the foundation points.
Some natural stones can be quite fragile and might break during drilling, we usually have a few extra stones on site just in case. Ensure your stones are level with one another by using a bunyip or a water pass level and adjust the stone capping thicknesses so that they are all even.
On contoured sites we allow each foundation to sit at a different level and we adjust the length of each pole to ensure that the building is straight.
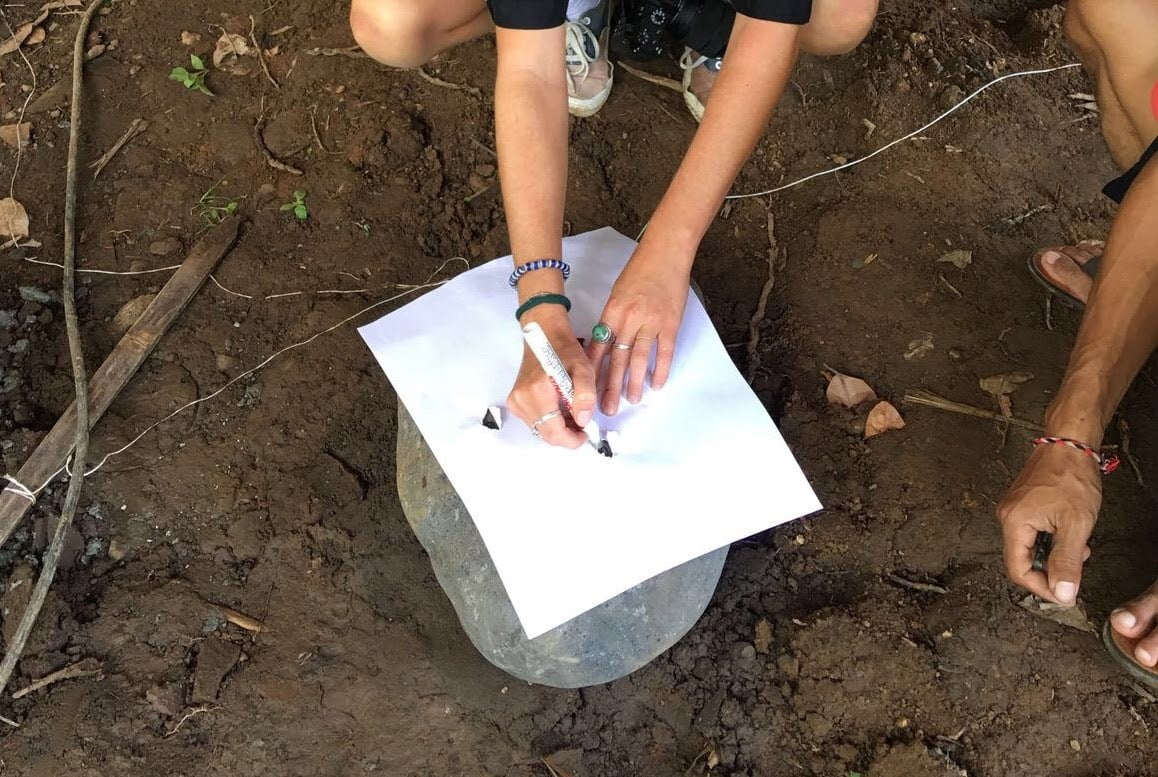
If you have 2 or more poles sitting on a single foundation, drill the holes by marking the spacing of the rebars on paper or plywood and using it as a reference to drilling holes on stones.
Always be careful while threading the stones over the rebars; a big team with good logistics is needed to lift and place big stones onto foundations.
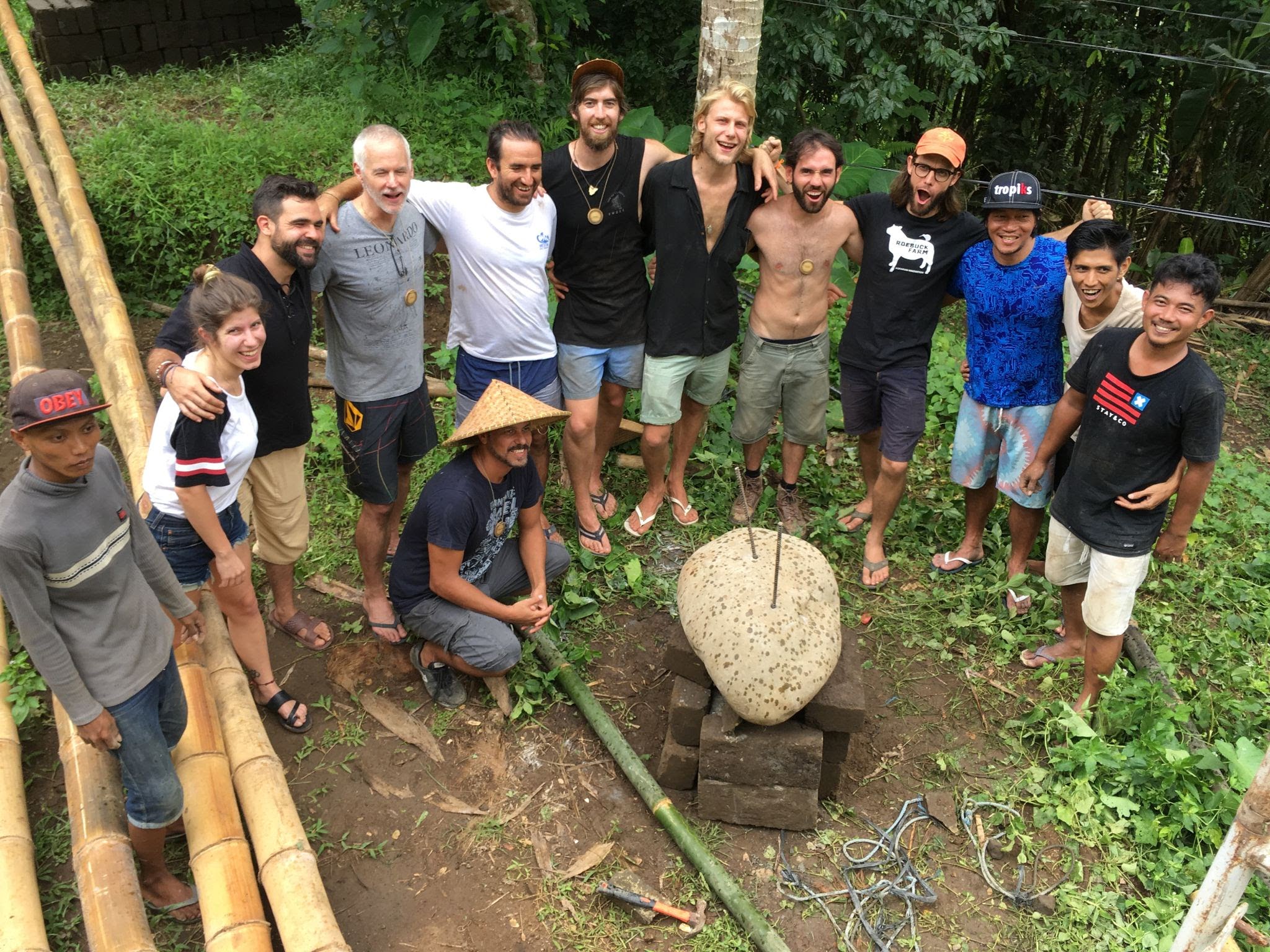
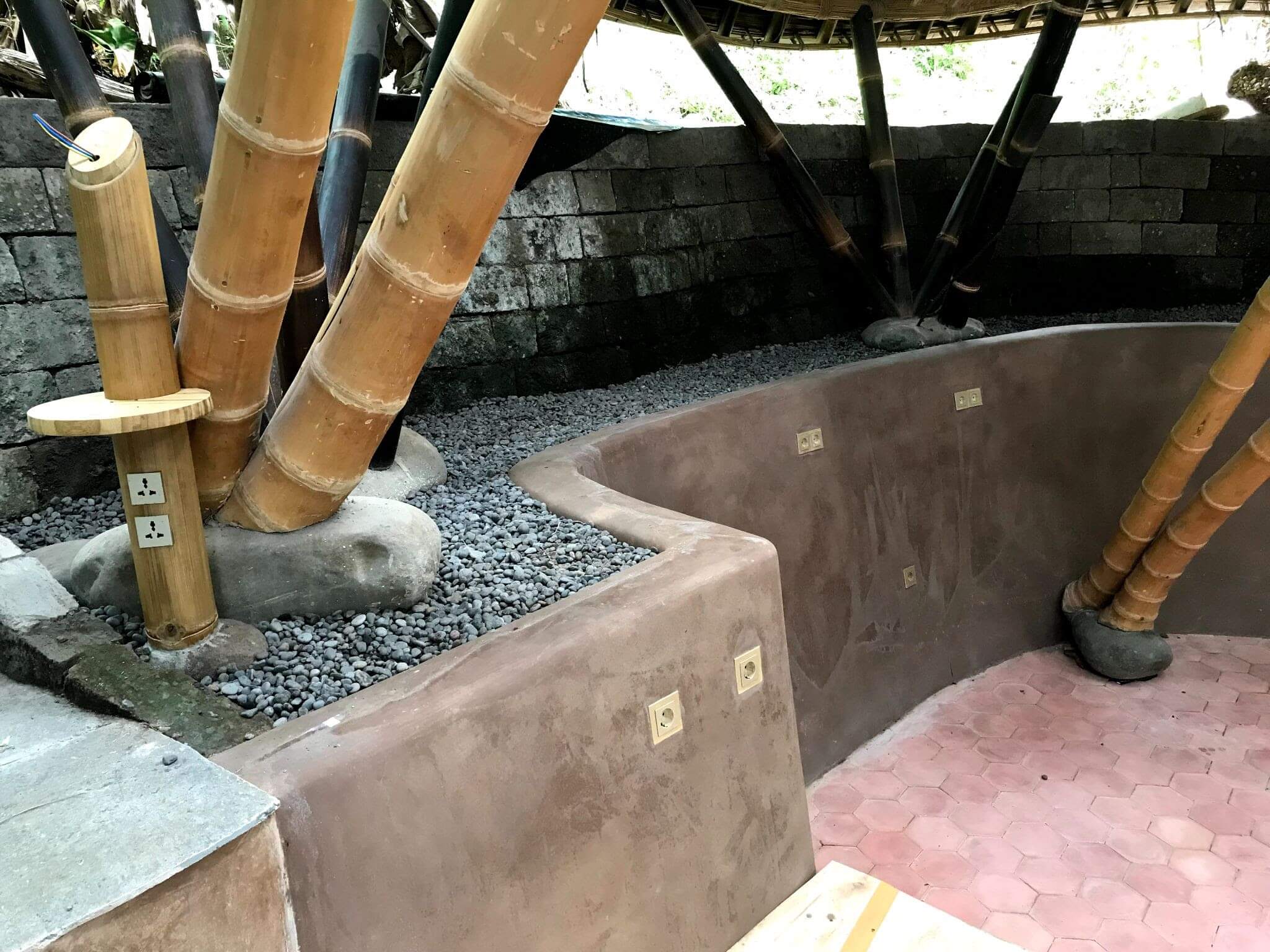














4. Fastening the bamboo poles to the foundations
The last step is to fasten the bamboo poles to the foundations. The center of the foundation contains a steel bar that is anchored into the concrete and will later act as the element fastening the bamboo pole to the foundation.
Bamboo is quite light so it's equally important that our foundations firmly fasten the building to the ground as it is for them to hold the building up, especially if there are strong winds in your location.
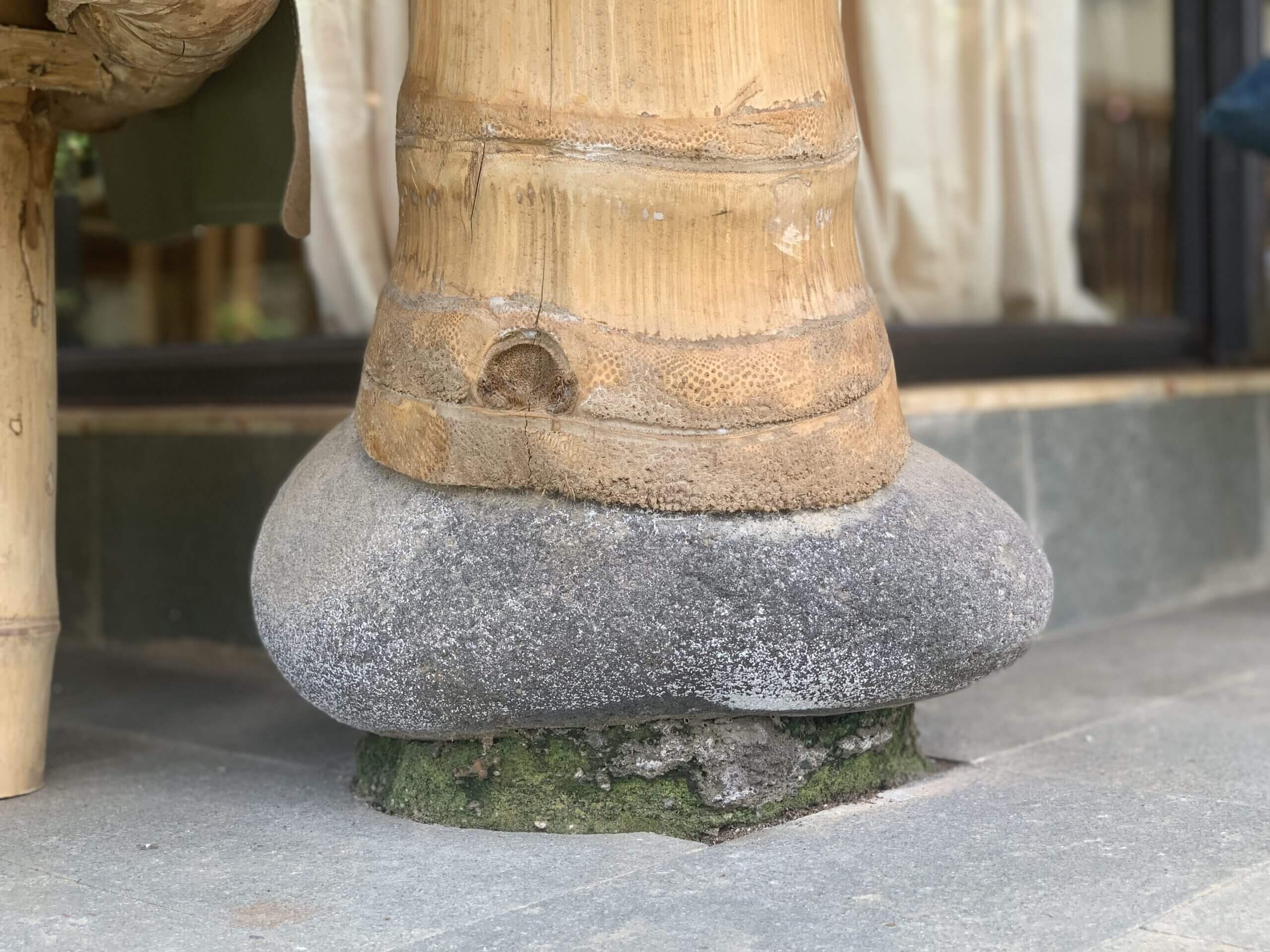
If natural stones are used as moisture barriers, the bottom of your bamboo that will sit on the river stones will need to be carved so that they can rest comfortably on the stone. If this is not done properly bamboo poles tend to crack due to uneven loads.
Once the main structural framing and roofing of the building are finished, the final step is fastening the bamboo structure to the foundations.
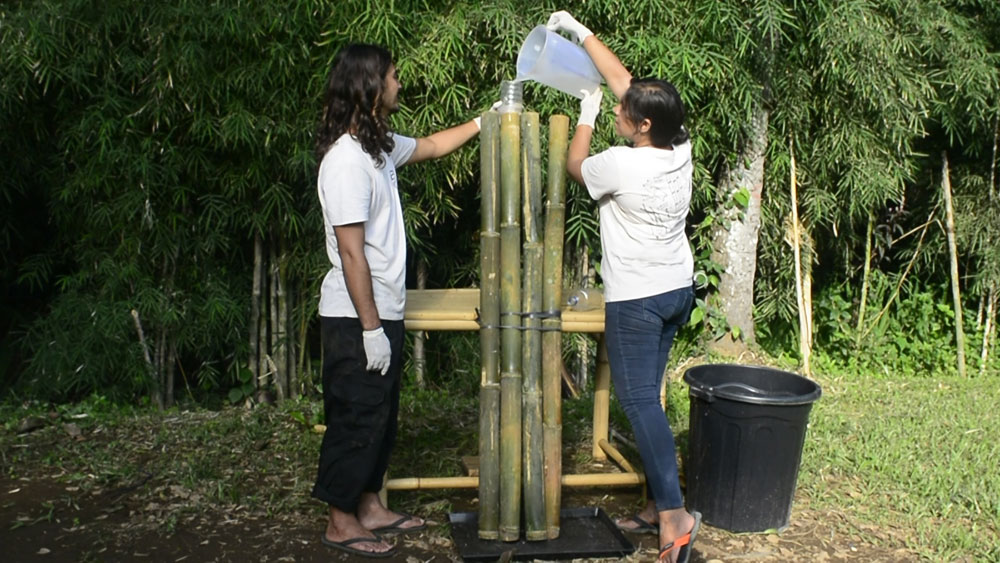
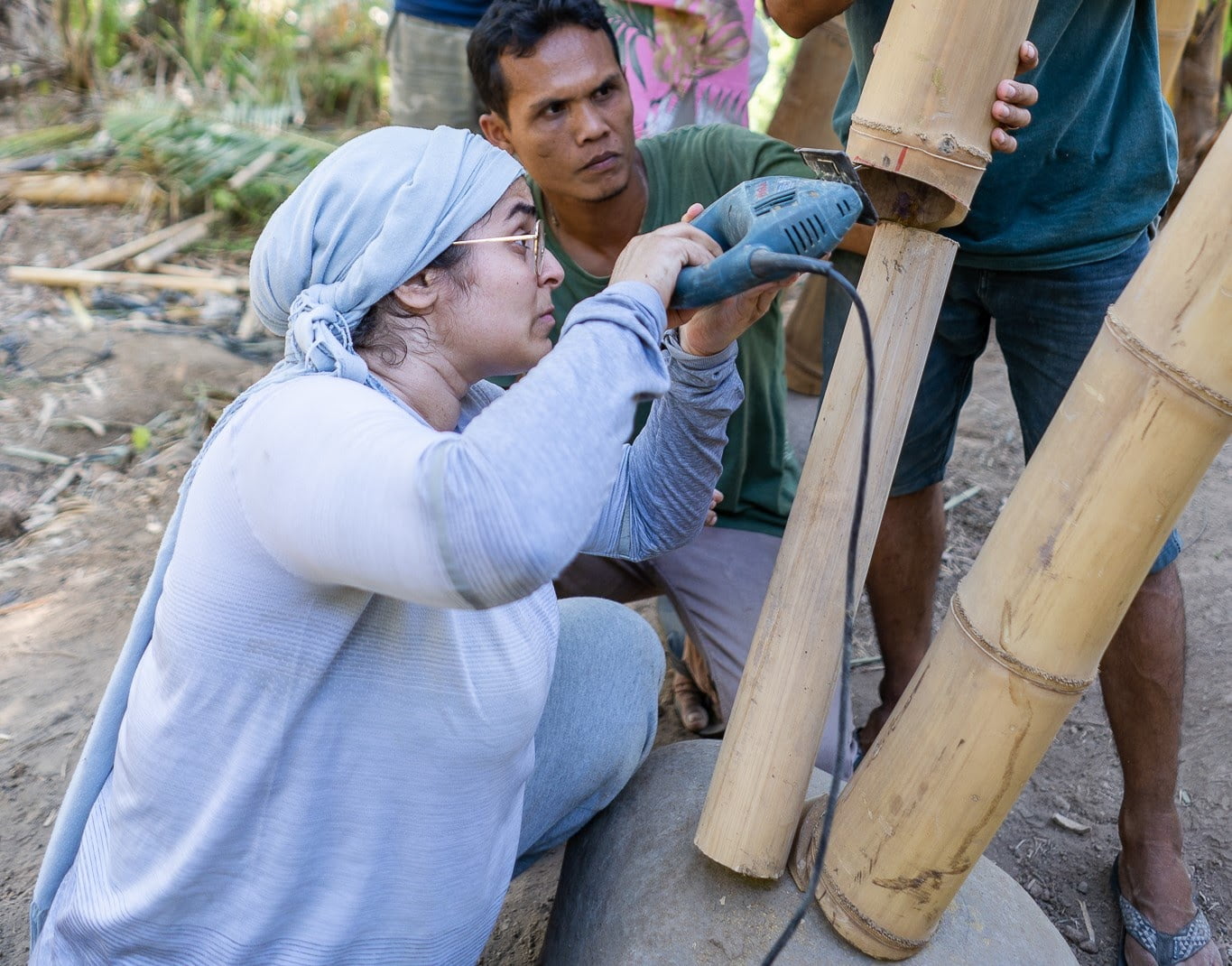
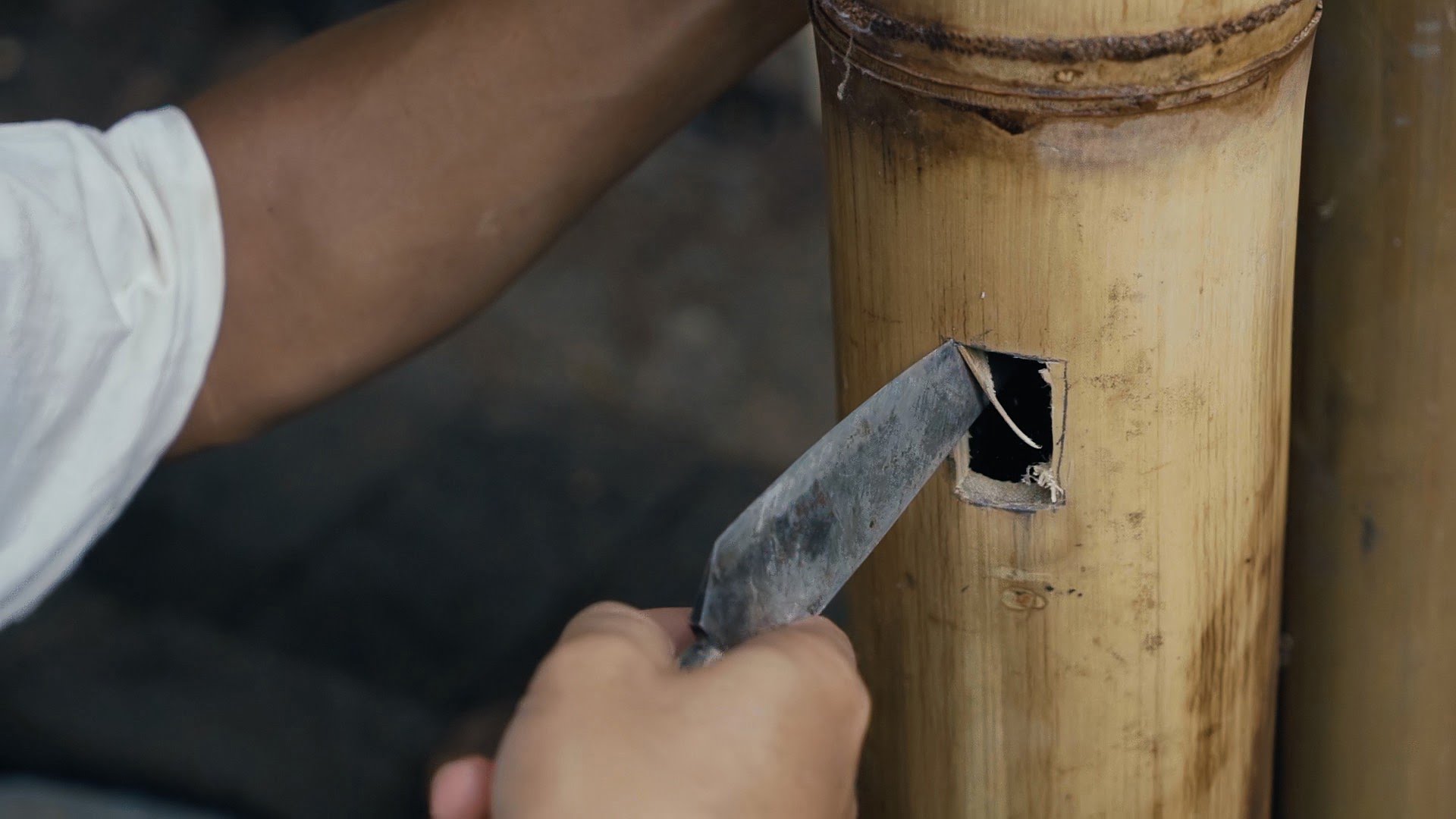
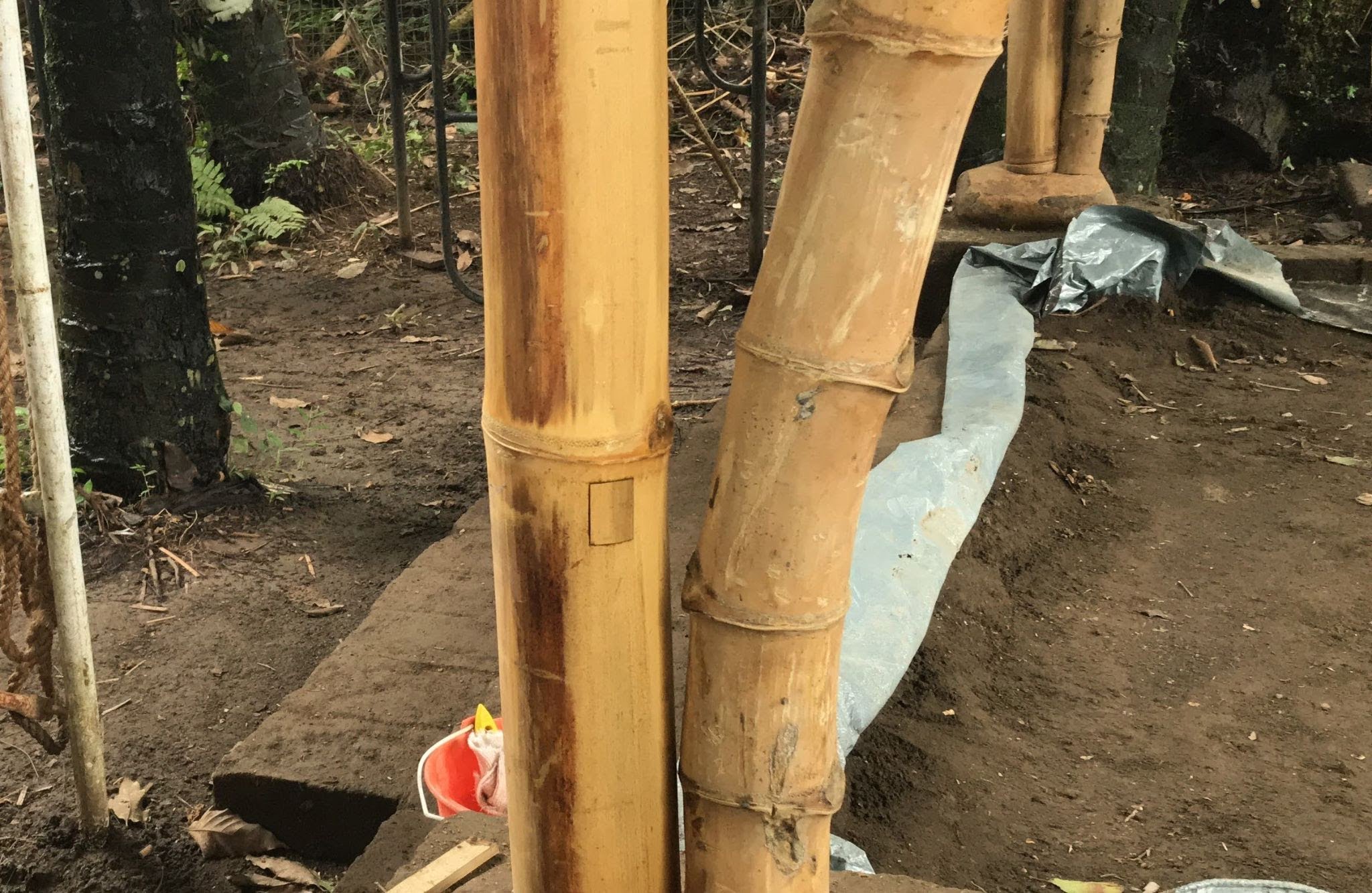
To do this, make a small hole in the side of the bamboo and prepare a mixture of concrete grouting. Then use a funnel to pour the concrete into the pole. Knock the side of the pole to encourage the concrete to settle in the bottom and remove any air pockets. The concrete is poured into the bamboo upto the level of the hole which is 50cm from the base. Finally, close the hole.


















During the Bamboo Online Immersion we cover all the basics you need to know about bamboo construction: from bamboo forestry, treatment, design and bamboo construction. Read more here: https://www.bamboou.com/online-immersion
Article by Sai Goutham and Maria Farrugia

Sai was the Research & Development Manager at Bamboo U until 2023. He is also a natural builder and an architect from India. He has managed many mud and bamboo projects over the years.
OCTOBER 10-21, 2025
The 11 Day Bamboo Build & Design Course in Bali
In 11 days, we'll show you how to build bamboo structures we’ll share all that it takes to build with nature.
Start Anytime
The Bamboo Harvesting Course
The Bamboo Harvesting Course is an online step-by-step training to harvest and care for your bamboo clumps to ensure their longevity and productivity. This maximizes the potential of this beautiful grass as a rapidly renewable resource.Whether you are an architect, builder, or sustainability enthusiast, this mini course will enable you to utilize this rapidly regenerative resource as a durable construction material.It will help remove any fear or doubt about the durability of bamboo and help you build reputable bamboo structures that stand the test of time!